 影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照Word文档格式.docx
影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照Word文档格式.docx
- 文档编号:19409959
- 上传时间:2023-01-06
- 格式:DOCX
- 页数:11
- 大小:332.82KB
影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照Word文档格式.docx
《影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照Word文档格式.docx》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照Word文档格式.docx(11页珍藏版)》请在冰豆网上搜索。
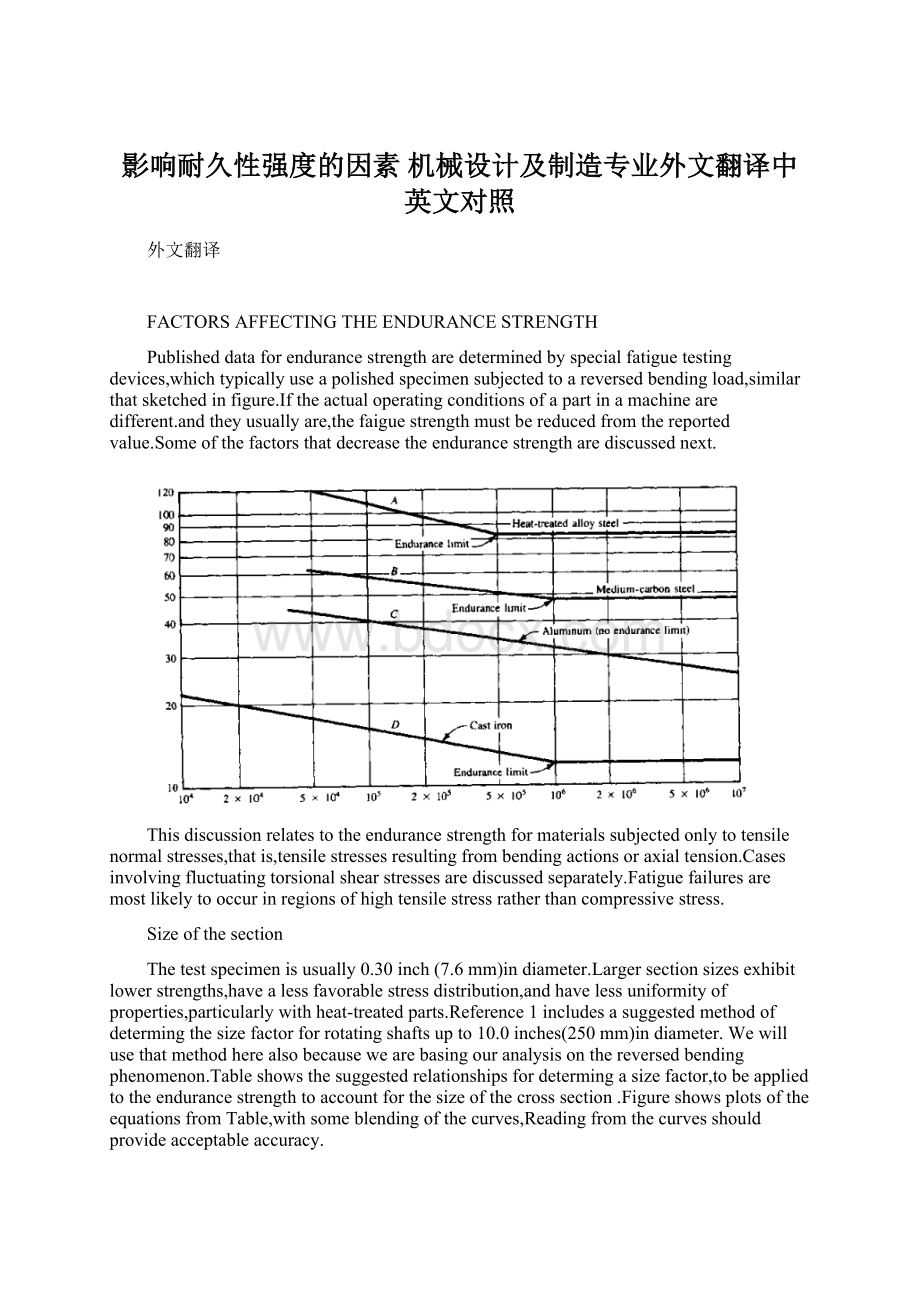
Sizeofthesection
Thetestspecimenisusually0.30inch(7.6mm)indiameter.Largersectionsizesexhibitlowerstrengths,havealessfavorablestressdistribution,andhavelessuniformityofproperties,particularlywithheat-treatedparts.Reference1includesasuggestedmethodofdetermingthesizefactorforrotatingshaftsupto10.0inches(250mm)indiameter.Wewillusethatmethodherealsobecausewearebasingouranalysisonthereversedbendingphenomenon.Tableshowsthesuggestedrelationshipsfordetermingasizefactor,tobeappliedtotheendurancestrengthtoaccountforthesizeofthecrosssection.FigureshowsplotsoftheequationsfromTable,withsomeblendingofthecurves,Readingfromthecurvesshouldprovideacceptableaccuracy.
Whenthecomponentbeingdesignedisnotcircularlikeashaft,judgmentisrequiredtodeterminethecharacteristicdimensiontouseintheformulas.Forflat,rolledshapes,thethicknessshouldbeused.Notedthattheuseoftheseequationsisapproximate.
SurfaceFinish
Anydeviationfromapolishedsurfacereducesendurancestrength.Figureshowsroughestimatesfortheendurancestrengths,comparedwiththeultimatetensilestrengthofsteelsforseveralpracticalsurfaceconditions,Itiscriticalthatpartssubjectedtofatigueloadingbeprotectedfromnicks,scratches,andcorrosionbecausetheydrasticallyreducefatiguestrength.
StressConcentrations
Suddenchangesingeometry,especiallysharpgroovesandnotcheswherehighstressconcentrationsoccur,arelikelyplacesforfatiguefailurestooccur.Careshouldbetakeninthedesignandmanufactureofcyclicallyloadedpartstokeepstressconcentrationfactorstoalowvalue.Wewillapplythestressconcentrationfactors,asfoundfromthemethodsofSection,tothecomputedstresses,ratherthantotheallowablestrengths.
Flaws
Internalflawsofthematerial,especiallylikelyincastparts,areplacesinwhichfatiguecracksinitiate.Criticalpartscanbeinspectedbyx-raytechniquesforinternalflaws,Iftheyarenotinspected,ahigher-than-averagedesignfactorshouldbespecifiedforcastparts,andalowerendurancestrengthshouldbeused.
Temperature
Mostmaterialshavealowerendurancesstrengthathightemperatures.Thereportedvaluesareforroomtemperatures.Operationabove160°
F(72°
C)willreducetheendurancestrengthofmostductilematerials.
NonuniformMaterialProperties
Manymaterialshavedifferentmaterialpropertiesindifferentdirectionsbecauseofthemannerinwhichthematerialwasprocessed.Rolledsheetorbarproductsaretypicallystrongerinthedirectionofrollingthantheyareinthetransversedirection.
Fatiguetestsarelikelyhavebeenrunontestbarsorientedinthestrongerdirection.Stressingofsuchmaterialinthetransversedirectionmayresultinlowerendurancestrength.
Nonuniformpropertiesarealsolikelytoexistinthevicinityofweldsbecauseofincompleteweldpenetration,slaginclusions,andvariationsinthegeometryofthepartattheweld.
Also.weldingofheat-treatedmaterialsmayalterthestrengthofthematerialbecauseoflocalannealingneartheweld.
Someweldingprocessesmayresultinthproductionofresidualtensilestressesthatdecreasetheeffectiveendurancestrengthofthematerial.
Annealingornormalizingafterweldingisoftenusedtorelievethesestresses,buttheeffectofsuchtreatmentsonthestrengthofthebasematerialmustbeconsidered.
ResidualStresses
Fatiguefailurestypicallyinitiateatlocationsofrelativelyhightensilestress.Grindingandmachining,especiallywithhighmaterialremovalrates,alsocauseundesirableresidualtensilestress.Weldinghasalreadybeenmentionedasaprocessthatmayproduceresidualtensilestress.
Anymanufacturingprocessthattendstoproduceresidualstresswilldecreasetheendurancestrengthofthecomponent.Criticalareasofcyclicallyloadedcomponentsshouldbemachinedorgroundinagentlefashion.Processesthatproduceresidualcompressivestressescanprovetobebenefical.Shotblastingandpeeningaretwosuchmethods.Shotblastingisperformedbydirectingahighvelocitystreamofhardenedballsorpelletsatthesurfacetobetreated.Peeningusesaseriesofhammerblowsonthesurface.Crankshafts,springs,andothercyclicallyloadedmachinepartscanbenefitfromthesemethods.
CorrosionandEnvironmentalFactors
Endurancestrengthdataaretypicallymeasuredwiththespecimeninair.Operatingconditionsthatexposeacomponenttowater,saltsolutions,orothercorrosiveenvironmentscansignificantlyreducetheeffectiveendurancestrength.Corrosionmaycauseharmfullocalsurfaceroughnessandmayalsoaltertheinternalgrainstructureandchemistryofehematerial.Steelsexposedtohydrogenareespeciallyaffectedadversely.
Nitriding
Nitridingisasurface-hardeningprocessforalloysteelsinwhichthematerialisheatedto950°
F(514°
C)inanitrogenatmosphere,typicallyammoniagas,followedbyslowcooling.Impvovementofendurancestrengthof50%ormorecanbeachievedwithnitriding.
WroughtversusCastMaterials
Metalalloyshavingsimilarchemicalcompositionscanbeeitherwroughtorcasttoproducethefinalform.Wroughtmaterialsareusuallyrolledordrawn.Wroughtmaterialsusuallyhaveahigherendurancestrengththancastmaterialsofsimilarcompositioninregionswherenosignificantstressconcentrationexits.However,inthevicinityofnotchesandotherdiscontinuities,theendurancestrengthofwroughtandcastmaterialsismorenearlyequal.Onepossibleexplanationofthisphenomenonisthatthecastmaterialislikelytohavemoreisotropicmaterialpropertiesthanthewroughtmaterialandislessaffectedbythepresenceofthestressconcentration.
Tousethemoreconservativeapproach,itisrecommendedthatafactorof0.8beappliedtothebasicendurancestrengthifacaststeelisused.Forcastiron,afactorof0.70isrecommended.
TypeofStress
Endurancestrengthdataareobtainedfromtherotatingbeamtestthatproducescompletelyreversedandrepeatednormalstresses.Themaximumstressisproductedatthesurfaceofthespecimen,andthestressvaneslinearlytozeroatthecenterofthecircularcrosssection.Iftheactualloadingisdifferentfrombending,afactorforthetypeofloadingshouldbeappliedtotheendurancestrength.
AxialTension
Underpuretension,allofthematerial--notjustthesurface—issubjectedtothemaximumstress.Afactorof0.80issuggestedtobethebendingendurancestrengthtoreflectthisdifferentbehavior.
EffectofStressRatioonEnduranceStrength
Figure5-10showsthegeneralvariationofendurance-strengthdataforagivenmaterialwhenthestressratioRvariesfrom-1.0to+1.0,coveringtherangeofcasesincludingthefollowing:
■Repeated,reversedstress(Figure5-3);
R=-1.0
■Partiallyreversedfluctuatingstresswithatensilemeanstress【Figure5-4(b)】;
-1.0<
R<
0
■Repeated,one-directiontensilestress(Figure5-6);
R=0
■Fluctuatingtensilestress【Figure5-4(a)】;
0<
1.0
■Staticstress(Figure5-1);
R=1
NotethatFigure5-10isonlyanexample,anditshouldnotbeusedtodetermineactualdatapoints.Ifsuchdataaredesiredforaparticularmaterial,specificdataforthatmaterialmustbefoundeitherexperimentallyorpublishedliterature.
Themostdamagingkindofstressamongthoselistedistherepeated,reversedstresswithR=-1.(SeeReference2.page27.)RecallthattherotatingshaftinbendingasshowninFigure5-2isanexampleofaload-carryingmembersubjectedtoastressratioR=-1.
FluctuatingstresseswithacompressivemeanstressasshowninParts(c)and(d)ofFigure5-4donotsignificantlyaffecttheendurancestrengthofthematerialbecausefatiguefailurestendtooriginateinregionsoftensilestress.
NotethatthecurvesofFigure5-10showestimateoftheendurancestrength,Sn,asafunctionoftheultimatetensilestrengthforsteel.Thesedataapplytoidealpolishedspecimensanddonotincludeanyofetheotherfactorsdiscussedinthissection.Forexample,thecurveforR=-1.0(reversedbending)showsthattheendurancestrengthforsteelisapproximately0.5timestheultimatestrength(0.50×
Sn)forlargenumbersofcyclesofloading(approximately10orhigher).Thisisagoodgeneralestimateforsteels.ThechartalsoshowsthattypesofloadproducingRgreaterthan-1.0butlessthan1.0havelessofaneffectontheendurancestrength.Thisillustratesthatusingdatafromthereversedbendingtestisthemostconservative.
WewillnotuseFigure5-10directlyforprobleminthisbookbecauseourprocedureforestimatingtheactualendurancestrengthstartswiththeuseofFigure5-9whichpresentsdatafromreversedbendingtests.Therefore,theeffectofstressratioisalreadyincluded.Section5-9ofthischapterincludesmethodsofanalysisforloadingcasesinwhichthefluctuatingstressproducesastressratiodifferentfromR=
- 配套讲稿:
如PPT文件的首页显示word图标,表示该PPT已包含配套word讲稿。双击word图标可打开word文档。
- 特殊限制:
部分文档作品中含有的国旗、国徽等图片,仅作为作品整体效果示例展示,禁止商用。设计者仅对作品中独创性部分享有著作权。
- 关 键 词:
- 影响耐久性强度的因素 机械设计及制造专业外文翻译中英文对照 影响 耐久性 强度 因素 机械设计 制造 专业 外文 翻译 中英文 对照
 冰豆网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
冰豆网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。


 铝散热器项目年度预算报告.docx
铝散热器项目年度预算报告.docx
 血液的一般检验4_精品文档.ppt
血液的一般检验4_精品文档.ppt
